What is Down syndrome? What causes Down syndrome in babies? What are the sign and symptoms of Down syndrome in babies? Does Down syndrome affect the baby for the worse? Are you aware of the answers to these questions? If not, here are the facts about Down syndrome.
Down syndrome (R) is a disorder that affects a baby’s physical and psychological well being. Down syndrome is all about the mutation in the genes of the child.
By the end of the article, you will get to know the facts about Down syndrome and the behavioral characteristics of Down syndrome in babies. You will also get to know the various ways to prevent Down syndrome in babies.
What Is Down Syndrome?
As we know, genes carry the codes responsible for all of our inherited traits and are grouped along with rod-like structures called chromosomes. The nucleus of each cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, half of the chromosomes are transferred from each parent. Down syndrome occurs when a baby has a full or partial extra copy of chromosome 21.
This course of development and the characteristic is known as Down syndrome. Each and every baby born with Down syndrome is born different. Down syndrome is a disorder that affects the babies physical, psychological as well as intellectual disability.
The extra genetic material causes the developmental changes and physical changes in the Down syndrome. Down syndrome is otherwise known as trisomy 21.
It’s one of the most common genetic chromosomal disorders and can cause learning disabilities in children. It also causes other medical abnormalities, including heart and gastrointestinal disorders.
How Common Is Down Syndrome?

According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, one in every 700 babies in the United States is born with Down syndrome. Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal condition in babies. About 6,000 babies with Down syndrome are born in the United States each year.
According to the Genetics Home Reference, Down syndrome occurs in about 1 in 800 newborns. About 5,300 babies with Down syndrome are born in the United States each year, and approximately 200,000 people in this country have the condition. Although women of any age can have a child with Down syndrome, the chance of having a child with this condition increases as a woman gets older.
Before the age of 30, Down syndrome occurs in fewer than 1 in 1,000 (R) pregnancies. After the age of 40, this figure rises to about 12 in 1,000.
Types Of Down Syndrome:

There are three types of Down syndrome which include:
1. Trisomy 21:
This is the most common form of Down syndrome. About 95% of children with Down syndrome have Trisomy 21. In this type of Down syndrome, each cell in the body has 3 separate copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual 2 copies. That means there is an extra pair of chromosome in the human body.
This down syndrome is known as “nondisjunction”. This is caused due to an error in cell division. Prior to or at conception, a pair of 21st chromosomes in either the sperm or the egg fails to separate. As the embryo develops, the extra chromosome is replicated in every cell of the body.
2. Translocation Down Syndrome:
This type accounts for a small percentage of people with Down syndrome (about 3%). This occurs when an extra part or a whole extra chromosome 21 is present, but it is attached or “trans-located” to a different chromosome rather than being a separate chromosome 21.
There are 46 total chromosomes and one of them has an extra piece of chromosome 21 attached. An additional full or partial copy of chromosome 21 attaches to another chromosome, usually chromosome 14.
3. Mosaic Down Syndrome:
Mosaic is a mixture of two types of cell. This type affects about 2% of the people with Down syndrome. Mosaic means mixture or combination. For children with mosaic Down syndrome, some of their cells have 3 copies of chromosome 21, but other cells have the typical two copies of chromosome 21.
Children with mosaic Down syndrome (R) have the same features as other children with Down syndrome. They may have fewer features of the condition due to the presence of some (or many) cells with a typical number of chromosomes.
What Causes Down Syndrome In Babies?

Regardless of the types of Down syndrome, the abnormalities or absence of chromosomes 21 is the primary cause of Down syndrome in babies.
Some of the causes behind Down syndrome are as follows-
1. Multiple Copies Of Chromosomes 21:
This is the first and foremost cause behind Down syndrome. This is referred as Trisomy 21. About 95% of babies are born with this form of Down syndrome. In this, there are three copies of chromosomes 21.
This is caused due to an error in cell division. It occurs at conception or prior to it, a pair of 21st chromosomes in either the sperm or the egg fails to separate. As the embryo develops, at the phase of conception the extra chromosome is replicated in every cell of the babies body.
2. Broken Chromosome:
This form of Down syndrome is caused when the baby is born only with a broken chromosome 21. The broken part of the chromosome 21 attaches itself to chromosome 14, leaving the chromosome 21 incomplete and the 14th chromosome with an extra attachment.
3. Genetic Maturation:
Down syndrome can be caused due to genetic maturation. It happens due to genetic maturation in the egg or sperm. Any one of the parents can transmit the genetic maturation to their child.
4. Mothers Age:
One of the major factors that increase the risk of having a baby with Down syndrome is the mother’s age. Women who are 35 years or older are more likely to have a pregnancy affected by Down syndrome than women who become pregnant at a younger age.
What Are The Risk Factors For Down Syndrome?
Women who are 35 years or older are more likely to have a pregnancy affected by Down syndrome than women who become pregnant at a younger age.
The table shows you the chances of Down syndrome at different marital age-
| MATERNAL AGE | RISK |
| 30 | 1 in 900 |
| 31 | 1 in 800 |
| 32 | 1 in 720 |
| 33 | 1 in 600 |
| 34 | 1 in 450 |
| 35 | 1 in 350 |
| 36 | 1 in 300 |
| 37 | 1 in 250 |
| 38 | 1 in 200 |
| 39 | 1 in 150 |
| 40 | 1 in 100 |
| 41 | 1 in 80 |
| 42 | 1 in 70 |
| 43 | 1 in 50 |
| 44 | 1 in 40 |
| 45 | 1 in 30 |
| 46 | 1 in 25 |
| 47 | 1 in 20 |
| 48 | 1 in 15 |
| 49 | 1 in 10 |
Sign And Symptoms Of Down Syndrome In Babies;
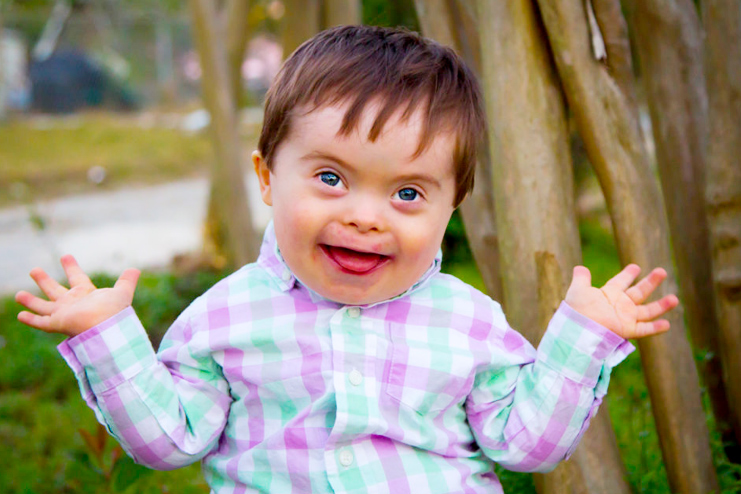

The sign and symptoms (R) of Down syndrome in babies include:
Some of the physical features of Down Syndrome include:
- A flattened face, especially the bridge of the nose
- Almond-shaped eyes that slant up
- A short neck
- Small ears
- A tongue that tends to stick out of the mouth
- Tiny white spots on the iris of the eye
- Small hands and feet
- A single line across the palm of the hand
- Small pinky fingers that sometimes curve toward the thumb
- Poor muscle tone or loose joints
- Shorter in height as children and adults
- Excessive flexible
- Upward slanting eye lids
- A large space between the large and second toe.
Effects Of Down Syndrome In Babies

There are a lot of negative effects of Down syndrome in babies, such as-
Developmental Delay:
The children with Down syndrome will be having difficulties in their cognitive development. This may vary from mild to moderate. The level of cognitive development will vary from one child to another who is suffering from Down syndrome.
Children with Down syndrome often reach developmental milestones a little later than their peers of that particular age. They are mostly delayed in learning to talk, walk, speak, etc. The children with down syndrome need speech therapy in order to learn the expressive language.
Fine motor skills may also be delayed. They can take time to develop after the child acquires gross motor skills. On average, a child with Down syndrome will adopt as follows-
- sit at 11 months
- crawl at 17 months
- walk at 26 months
There may also be problems with attention, a tendency to make poor judgments, and impulsive behavior. The babies with Down syndrome can attend school and become active, valued members of the community with proper guidance through their life.
Health issues
There are health problems that can affect any organ system or bodily function of the babies. There are also be a higher risk of-
- respiratory problems
- hearing difficulties
- Alzheimer’s disease
- childhood leukemia (R)
- epilepsy
- thyroid conditions
- Obstructive sleep apnea (R)
- Ear infection
- Eye diseases
- Heart defects present at birth
Behavioral Characteristic Of Down Syndrome In Babies;

The behavioral characteristic of Down syndrome in babies are as follows-
- impulsive behavior
- poor judgment
- short attention span
- slow learning capabilities
- Delayed language and speech development.
Some of the other behavioral symptoms (R) are-
1. Trouble controlling impulses;
The children with Down syndrome often don’t notice the “stop signs” that tell them not to behave in that particular way.
2. Trouble communicating;
As the baby cannot express themselves or understand others easily, they become frustrated and irritated. Children with Down syndrome often have such difficulties as the studies suggest.
3. Trouble relating to other children and adults;
Children with Down syndrome are social and affectionate as several studies have proven. But often, they may not know how to play efficiently with peers. This leads the child to end up misbehaving.
4. Trouble managing frustration;
As mentioned above, children with Down syndrome have multiple reasons to be frustrated. Children with Down syndrome struggle to calm down and feel better when frustrations come up. This can worsen behavior problems.
How to Spot Down Syndrome In Babies?
Chromosome problems such as Down syndrome can often be diagnosed before birth when the fetus is still in the uterus. This is done by looking at cells in the amniotic fluid or from the placenta. This is a routine screening which is recommended by the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
It is done by looking at the amount of the baby’s DNA in the mother’s blood during the phase of pregnancy. This is a noninvasive prenatal screening. These tests are very accurate and followed by most of the doctors and pediatrician.
The ultrasound during pregnancy can also show the possibility or occurance of Down syndrome. But, it is believed that ultrasound is not 100% accurate. There may be a lot of problems from Down syndrome that may not be seen with ultrasound report or scan.
After birth, your baby may be diagnosed with a physical exam. It can be done by the healthcare provider also by taking the blood sample. This is checked in a lab to find the extra chromosome in the gene of the baby.
The Screening Test Include-
- Nuchal translucency testing: At 11–14 weeks, an ultrasound can measure the clear space in folds of tissue behind the neck of a developing fetus.
- Triple screen or quadruple screen: At 15–18 weeks, this measures the quantities of various substances in the mother’s blood.
- Integrated screen: This combines results from first-trimester blood and screening tests, with or without nuchal translucency, with second-trimester quadruple screening results.
- Cell-free DNA: This is a blood test that analyzes fetal DNA present in the mother’s blood.
- Genetic ultrasound: At 18–20 weeks, doctors combine a detailed ultrasound with blood test results.
Diagnostic tests include:
- Chorionic villus sampling: At 8–12 weeks, a doctor might obtain a tiny sample of placenta for analysis, using a needle inserted into the cervix or the abdomen.
- Amniocentesis: At 15–20 weeks, they may obtain a small amount of amniotic fluid (R) for analysis, using a needle inserted into the abdomen.
- Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling: After 20 weeks, the doctor may take a small sample of blood from the umbilical cord for analysis, using a needle inserted into the abdomen.
Is There A Cure For Down Syndrome?
There is no cure for Down syndrome. It is a life long condition. Research is still going on a large scale but doctors, scientists are still inconclusive with their answers with respect to how to cure or prevent the chromosome error.
A study suggests that some women who have had a baby with Down syndrome had an abnormality in how their body metabolizes, or processes, the B vitamin folic acid, etc.
This is the reason why a pregnant woman should take a daily multivitamin containing 400 micrograms of folic acid to reduce the risks for certain birth defects of the brain and spinal cord.
Various high doses of vitamins given to children with Down syndrome can improve the mental performance and lessen the degree of intellectual disability as mentioned by a few experts. But till date, no medical studies have proved that this actually works in case of Down syndrome baby development.
How To Prevent Down Syndrome In Babies?
There is no specific treatment for Down syndrome. Few children with Down syndrome can be treated through-
1. Surgery:
This is a way when the conditions of the baby like congenital heart defects and intestinal problems can be rectified through surgery soon after the baby is born.
2. Medication:
The Chronic problems like thyroid issues and constipation are alleviated with the help of medicines that help the organs function correctly.
3. Adequate immunization:
Vaccinating the baby as per schedule can reduce their susceptibility to infections.
4. Tools and Equipment:
This is the substitute that can help to manage the children with Down syndrome such as glasses can correct vision problems while hearing aids can help the child hear properly.
5. Lifestyle changes:
The children with Down syndrome are prone to obesity, so parents can consider specialized diet and exercises that help the little one maintain a healthy weight.
How To Care For A Child With Down Syndrome?
There are various ways to take care of Down syndrome newborn behavior.
Some of the ways are-
1. Give Simple and Clear Direction:
Language is often difficult for children with Down syndrome as we discussed prior in the article. The more complicated you speak, the less likely your child will understand what you want. So, directions should be specific, directive and contain the fewest steps possible. It should be a request, not a command.
2. Establish A Routine:
Much like how adults have routines, even the children with Down Syndrome should abide by one. The child is likely to do best when the day’s structure is the same as it was the day before. Try your best to make a routine and to help your child understand what that routine is all about so that they will able to do their stuff independently.
3. Make Time For Fun Stuff:
As the child is struggling with behavioral problems, they tend to get a lot of negative attention. Induce positive interactions with your child, even when things are at their worst. Make sure you take out time each day to play a game, read a book, draw, cook a fun dish, or watch a video with your child, no matter what the situation is all about.
4. Reward Good Behaviour:
This is an amazing way to take care of a child with Down syndrome. Always try to reward their good behavior. Setting up a system to reward the behavior will encourage the child to shows positive outcomes.
5. Plan For Difficult Sistution:
With structure, it gets better but we can’t always keep things the same. As a parent or caregiver, you know your child best. The parents are aware of some things that are difficult for the child as we all know. So, planning for these events can be helpful and you can help your child prepare for changes in order to reduce his or her worry or behavior problems.
FAQ’s

Can babies develop down syndrome after birth?
Down syndrome occurs due to an error in cell division. It occurs at conception or prior to it, a pair of 21st chromosomes in either the sperm or the egg fails to separate. As the embryo develops, at the phase of conception the extra chromosome is replicated in every cell of the babies body. Chromosome problems such as Down syndrome can often be diagnosed before birth when the fetus is still in the uterus. So, to answer the question, no, babies can’t develop Down Syndrome after birth but the same happens during the fetal stage itself.
Can Smoking Cause Down Syndrome In Babies?
There is less number of research on the effects of maternal smoking and Down syndrome in infants. But, most studies on the matter either lead to no conclusion or link between the two. Nevertheless, smoking is known to cause birth defects and experts recommend quitting smoking if you are pregnant or trying to conceive.
Can Babies With Down Syndrome Breastfeed?
Yes. Infants with Down syndrome can breastfeed but may have trouble suckling due to low muscle tone and may get tired sooner while breastfeeding. You can consult a doctor or pediatrician for further help or concern.
Down syndrome in children is not easy to deal with. The parents need a lot of courage and mental strength to take care of a newborn baby with Down syndrome. Well, I hope this article has given you all the answers to your doubts and queries regarding Down syndrome.









































